Quality manual, ISO 13485 and MDR, free template
The European regulation for medical devices requires manufacturers to write and maintain a quality manual that documents the quality management system implemented, as specified in Regulation (EU) 2017/745, Chapter I.2.2 and Annex XI.A.6.2 :
All the elements, requirements and provisions adopted by the manufacturer for its quality management system shall be documented in a systematic and orderly manner in the form of a quality manual and written policies and procedures such as quality programmes, quality plans and quality records.
In this article, you will find a quality manual template conforming to the requirements of Regulation 2017/745 and EN ISO 13485:2016 + A11:2021.
👉 This quality manual template can be set up according to your activities and products, using Qualitio online templates.
The quality manual is a document that presents the measures taken by an organization to meet the requirements applicable to its quality management system.
The quality manual allows to understand the functioning of a company and its environment and to communicate its objectives. It is often presented to auditors and new employees.
A quality manual should document all the elements adopted by the organization for its QMS.
General information
Presentation of the company
More detailed information can be added to the quality manual, beware: it will need to be kept up to date.
Examples:
- History of your company, this can be useful if the “regulatory” history is complex, with for example buy-outs/mergers, transfers of certificates, or changes in the scope of the QMS.
- Description of the clinical and market context (difficult if you have varied products)
- Identification of other organisations that may impact the conformity of your activities: critical subcontractors, distributors, certification body,…
- …
Example:
(Name of your company) is a company created in XXXX. It creates, develops and markets innovative medical devices on the market of (your industry).
- Organisation: See the document “Organisation chart of the company”.
- Market: (by country and/or by zone: EU, US…)
- Customers: the devices are sold to (your customers: hospitals, individuals, health professionals, other MD manufacturers, etc.)
- Our mission: to provide (your users) with products that guarantee a high level of (e.g. quality, safety, performance), to enable them to (the purpose of use of the device, its clinical benefits).
- Our capabilities: (describe your main activities e.g. design, market, maintain) a (the type of device you offer).
- Address: (your postal address)
Regulatory role(s) of the company
Within the framework of the applicable regulatory requirements, the company assumes the role of :
Example:
| Role of the company | Regulatory | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Regulation (EU) 2017/745 | Marketing of own-name MD in the EU. |
| Distributor | Regulation (EU) 2017/745 | Part of the supply chain of a MD from another manufacturer. |
| Manufacturer | Regulation (EU) 207/2012 | Marketing of own-name MD with provision of instructions for use only in electronic format. |
Other possible roles: agent or importer.
Role of the manual and scope of the QMS
Role of the quality manual
This quality manual contains the activities undertaken by (your company name) to fulfil our commitments to our customers and the applicable regulations.
It has been written so that all parties involved (e.g. customers, staff, authorities, shareholders, suppliers) can easily understand our organisation.
Scope of the QMS
Example:
The QMS scope includes the activities of design, production, distribution, installation, maintenance, eliminationof (the reference or family of your devices).
ISO 13485:2016 requirements not applicable
The following table identifies the requirements of ISO 13485:2016 that are not applicable to our company and justifies these non-applicabilities :
Example:
| § | Extract | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| 4.1.6 | The org. shall document p… | The company does not use software |
| 6.3 | As appropriate, the requi…. | The company does not use ECM in its operations |
| 6.4.1 | The org. shall document the r… | Environmental working conditions are not critical to the safety of employees, the outcome of their activities or products conformity |
| 6.4.2 | As appropriate, the org… | Working conditions and devices do not present a contamination risk to personnel or devices |
| 6.4.2 | For sterile MDs, the org…. | The device is not sterile |
| 7.3.1 | The org shall document p… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.2 | The org. shall plan and c… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.3 | Inputs relating to product … | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.4 | Design and development outputs shall… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.5 | At suitable stages, systematic reviews … | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.6 | Design and development verification shall… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.7 | Design and development validation shall… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.8 | The org shall document p… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.9 | The org shall document p… | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.3.10 | The org shall maintain a … | Quality assurance does not cover design activities |
| 7.5.2 | The org shall document the r… | Working conditions and devices do not present a contamination risk to personnel or devices |
| 7.5.3 | The org. shall document the r… | The company does not offer installation activity |
| 7.5.4 | If servicing of the medical device … | The company does not offer Servicing activities |
| 7.5.5 | The organization shall maintain r… | The device is not sterile |
| 7.5.6 | The org. must document p… | The company does not use computer software used in production, or the company does not provide services |
| 7.5.6 | Such software applications s… | The company does not use computer software used in production, or the company does not provide services |
| 7.5.6 | The specific approach and… | The company does not offer services |
| 7.5.6 | Records of the results and conclusion… | The company does not provide services |
| 7.5.7 | The organization shall document … | The device is not sterile |
| 7.5.9.2 | Particular requirements for implantable medical devices | The device is not implantable |
| 7.5.11 | The org. shall protect prod… | The working conditions and devices do not present a risk of contamination to personnel or devices |
| 7.6 | As necessary … | The company does not use ECM in its operations |
| 7.6 | The org. shall document p… | The company does not use software |
| 8.2.6 | As appropriate, records shall… | The org. does not use ECM as part of its operations |
| 8.2.6 | Product release and service delivery… | The company does not provide services |
| 8.2.6 | For implantable MDs, the… | The device is not implantable |
ISO 13485:2016 requirements excluded
Example :
| § | Justification | Standard used |
|---|---|---|
| 7.6 | Control of monitoring and measuring equipment | ISO 9001 certification + legal metrology |
Management commitment
Management commitments and references to evidence of implementation are summarised below :
Example :
| Commitment | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Ensure compliance with applicable regulatory and normative requirements | Definition of the tasks of the person responsible for ensuring compliance with regulations.List of regulations followed by the company (see 📰 Watch • ISO standards) Management of Normative and Regulatory Requirements according to ▶️ Procedure • Management of Normative and Regulatory Requirements |
| Ensure that responsibilities and authorities are defined documented and communicated | Process and activity planning (e.g. 📅 Plan • Usability Engineering)”Company organisation chart””Job cards” and “Staff cards” according to ▶️ Procedure • Human Resources Management |
| Ensuring the availability of resources | Process and activity planning (e.g. 📅 Plan • Usability Engineering)Human resources management according to ▶️ Procedure • Human Resources ManagementInfrastructure and work environment management according to ▶️ Procedure • Infrastructure and Working Environment |
| Ensuring the qualification of staff with regard to responsibilities | Management of human resources and training needs according to ▶️ Procedure • Human Resources Management |
| Maintain process adequacy and QMS effectiveness | Measure and improve effectiveness: ▶️ Procedure • Measurement, Analysis and ImprovementManage non-conformities and CAPAs: ▶️ Procedure • Non-Conformities and Preventive and Corrective Actions (NC, CAPA)Management review: ▶️ Procedure • Management Reviews |
| Defining a policy to define and review risk acceptability criteria | A general policy is given in ▶️ Procedure • Risk Management, it is adapted to each project and expressed in the planning document 📅 Plan • Risk Management ▶️ Procedure • Benefit / Risk evaluation |
| Ensure compliance with customer requirements | Customer requirements are taken into account according to ▶️ Procedure • Customer Requirements Management. |
| Implement approved QMS | Appropriateness of the system is demonstrated by maintaining certificates. See audit reports. |
Quality policy
The quality policy includes :
- Compliance with regulatory requirements,
- Maintaining the effectiveness of the QMS, and
- The improvement of products and activities through monitoring activities.
The quality objectives are derived from this policy.
Example :
Our Quality Management System has been defined to comply with the applicable regulatory requirements for medical devices:
- Regulation (EU) 2017/745;
- National regulations “XXXXXX”.
Our policy is to serve the patient, to propose innovative devices using the latest advances in (your technical branch) to be able to (summary of intended use) and thus bring (summary of patient benefits) to the patient.
The implementation of this policy is based on the quality system put in place founded on:
- Customer satisfaction,
- Compliance with regulatory and legal requirements,
- Staff involvement and
- The sustainability of the company.
Quality objectives
The quality objectives are broken down by process and are associated with indicators described in the document “Table of quality objectives”.
Risk-based approach
The company applies a risk-based approach to the control of its activities. The resources implemented are proportionate to the level of risk assessed according to appropriate criteria.
This risk-based approach is detailed in the ▶️ Procedure • Risk-based approach.
Process approach
The processes are described in the “Process sheets”.
Interactions/Process mapping
Example:
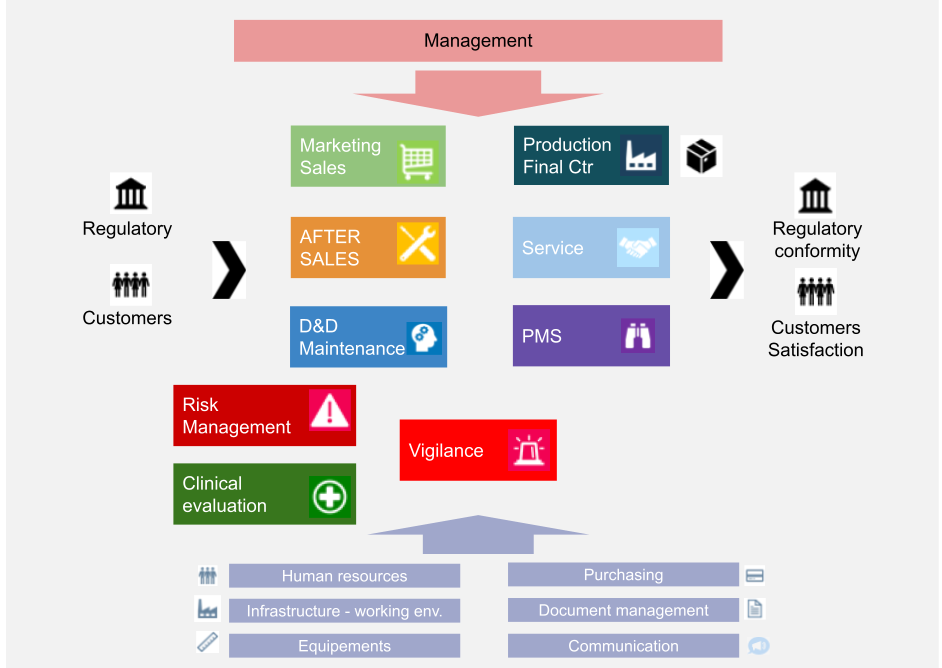
Process management
The methods used to ensure the effective operation and monitoring of processes use indicators described in the “Quality Objectives Table” document and are based on, but not limited to:
Example:
- Meetings;
- Internal audits;
- Management reviews; and
- Any other useful means.
Resources
Management makes every effort to ensure the availability of resources.
These resources include :
- Human resources, the management of which is described in ▶️ Procedure • Human Resources Management.
- Infrastructure and working environments, the management of which is described in ▶️ Procedure • Infrastructure and Working Environment.
- Purchases, the management of which is described in ▶️ Procedure • Purchasing Management.
- The information necessary for the operation and monitoring of the processes is available through the documents and records managed in accordance with the ▶️ Procedure • Document Management procedure.
Outsourced processes
The outsourced processes having an impact on product conformity are monitored and controlled according to the ▶️ Procedure • Measurement, Analysis and Improvement and ▶️ Procedure • Purchasing Management.
Where applicable: arrangements are contracted with the subcontractor.
List of QMS documents
The list of QMS documents is recorded in document XXX which contains the following fields:
Example :
- Type (procedure; review; operating mode; report; form; indicator; guide; list…);
- Reference;
- Title;
- Current version;
- Date of application;
- Location of the original;
- Location of copies;
- Retention period of outdated versions;
- Retention period of associated records;
- Method of destruction.
Document structure
The document system is organised as follows :
- The Quality Manual describes the Quality Management System;
- The Procedures describe the breakdown of the process and guarantee its quality;
- The Work Instructions and Operating Procedures describe the tasks of the process;
- The Forms and Documents are the media used to record data;
- The Records are used to provide evidence of conformity to requirements and effective operation of the quality management system.
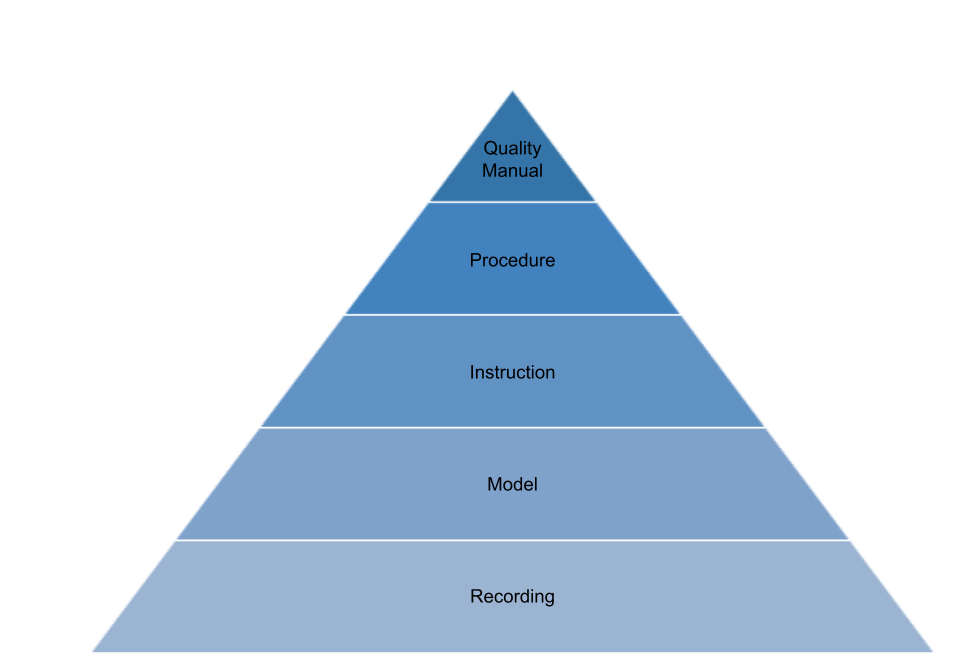
The identification of records is described in the ▶️ Procedure • Document Management.
Management review
Management reviews the QMS according to ▶️ Procedure • Management Reviews to ensure that it is still appropriate, adequate and effective.
